Liver directed therapy: treatments for colorectal cancer metastasis
What is liver directed therapy?
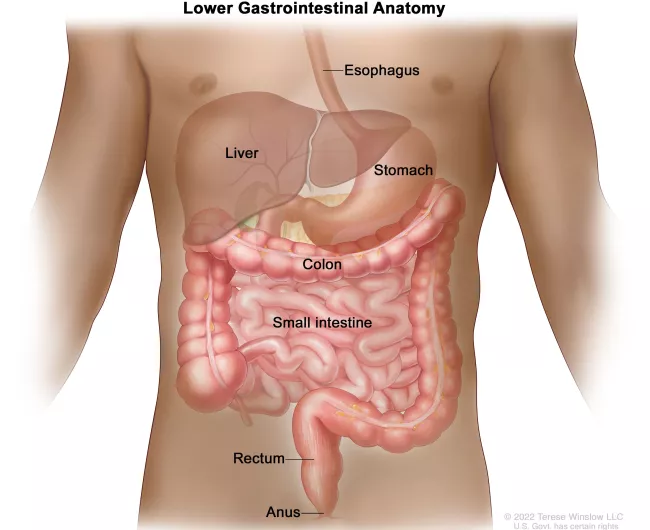
Colorectal cancer can spread to other parts of your body through your blood or lymphatic system. The liver is the most common site of metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer, due to the blood supply that exists between the large intestine and the liver.
While liver metastasis can be very challenging to stop, there are options to consider for treatment.
Surgery can play an important role in treating liver metastasis for many patients. However, not everyone is a candidate for liver surgery.
There are a number of therapies that use chemotherapy, HAI therapy, ablation, radiation, cryotherapy, heat, and other approaches to reduce or remove liver metastases.
Because liver directed therapies are localized and target just the tumor, much of the surrounding tissue is spared. Many of these therapies are minimally invasive and have a short recovery time.
Approved liver directed therapies
Read more
HAI TherapyTop resources

EPIC Act to Advance New CRC Therapies Needs Support
The EPIC Act would encourage investment in clinical trials for additional uses of existing drugs.

Michelle Cappel: Biomarker testing extends life
Michelle Cappel owes a lot to colorectal cancer biomarker testing — seven years of life and counting.

Don Shippey: from stage IV to six years cancer-free after receiving HAI pump
Don Shippey was 55 years old in 2016 when he decided he’d been putting off his colonoscopy long enough.





